ALWAYS
LAB-TESTED
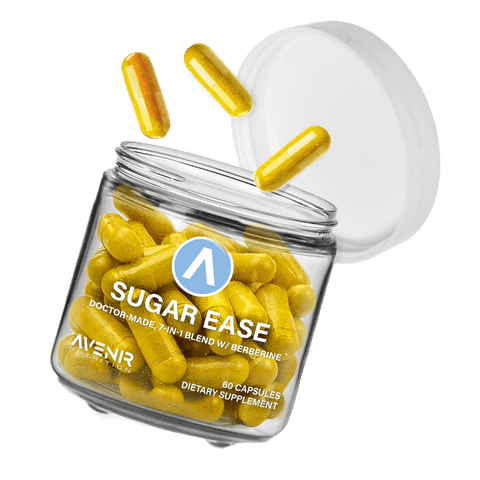
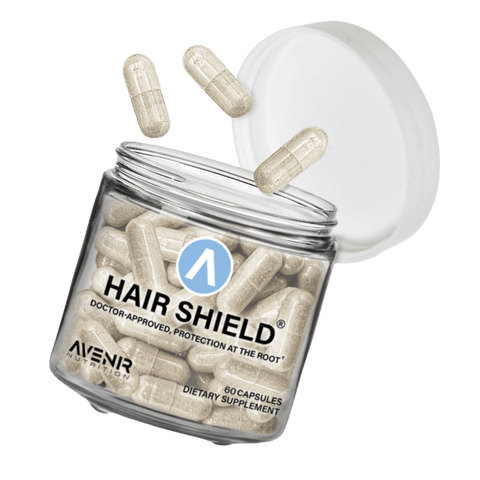
high-Quality
Ingredients
CREATED BY
PHYSICIANS
RESULTS
YOU FEEL
Invest in Your Health. Redefine Your Limits
Shop Avenir’s full range of premium nutraceuticals
Supercharge your health, energy & performance
Shop nutraceutical supplements for a life without limits
Physician-Created. Research-Backed. Quality-Assured.
Get a powerful health boost with nutraceuticals you can rely on.
-

SUPERIOR INGREDIENTS
Avenir’s nutraceutical products are all rigorously lab-tested for potency and purity
-

SUPERIOR SOURCING
Our proprietary formulations blend the highest-quality ingredients from around the world.
-

SUPERIOR SATISFACTION
See real results and benefits, or your money back!
Try Avenir Risk-Free Today
We put your satisfaction at the heart of everything we do
money-back guarantee
If our supplements don’t satisfy you, we’ll give you a full refund.
THOUSANDS OF SATISFIED CUSTOMERS
People love our products! Check out our reviews to see for yourself.
fast + free shipping
Shipping is always free (USA only), and your order will reach you within 3-4 days.
Check out what people are saying about Avenir
Real reviews from happy customers worldwide
Your Satisfaction, Guaranteed
All our nutraceuticals are returnable (no questions asked), so you can shop with confidence.
Avenir is dedicated to customer satisfaction. If you have questions or concerns, drop us a line. We’re here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
Need more info? Find what you’re looking for here!
At Avenir, we differentiate ourselves not by chasing health trends or merely introducing new products. Instead, we harness the power of existing clinical research, combined with the unparalleled expertise of our physician partners, to meticulously formulate nutraceutical blends optimized for specific health verticals. Quality is paramount. We ensure every product is crafted from the highest quality ingredients rigorously tested for purity, potency, and excellence. This commitment is our promise to deliver real results – or your money back.
Orders are processed within 1-2 business days, excluding weekends and holidays. After shipping, you'll receive a notification with a tracking number; allow 48 hours for tracking info to update.
All USA orders get free shipping. We also offer international shipping—options available at checkout.
If your order hasn't arrived within 7 days of the shipping email, contact support@email.com with your details.
Our return policy allows for returns on unopened bottles, while opened bottles are not eligible for return.
Subscription orders are not entitled to a refund.
To start a return, you can contact us at support@avenirnutrition.com. Items sent back to us without first requesting a return will not be accepted.
All of our products are safe to use on a daily basis. If you are on medication, are pregnant, or have any specific health conditions, please speak to your physician before you try Avenir products.
All of our products are formulated, encapsulated, and bottled in the USA under GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) badges, allowing us to deliver the highest quality supplements to our customers.
Join The Avenir Community
Access Dr. Sood’s health newsletter and be first in line for exclusive discounts and offers.
We promise not to spam you or share your information.